In this blog, we discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatments of gum disease. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease or periodontitis is a common yet serious oral health problem that affects millions of people worldwide. Gum disease can lead to tooth loss and other health issues if left untreated.
Whether you are experiencing symptoms or want to learn more about gum disease, this blog will provide you with valuable insights and information to help you maintain good oral health.
If you are searching for a teeth whitening dentist in Shepparton who will care for your oral health needs, visit us at Knight Street Dentists. Contact us today to book an appointment.
What is periodontal disease/gum disease?
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a serious oral health condition caused by an infection in the gums. If left untreated, it can damage the soft tissue and bone that supports your teeth, ultimately leading to loose teeth or even tooth loss.
The good news is that periodontitis is largely preventable with good oral hygiene practices. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, and seeing your dentist regularly for checkups can greatly reduce your risk of developing gum disease. And if you do have periodontitis, early detection and treatment can help prevent further damage to your gums and teeth. So, let’s take care of our oral health and keep those beautiful smiles healthy and strong!
Gum problem symptoms
Healthy gums will be firm and pale pink, and they will fit tightly around your teeth. Here are some of the symptoms that your gums aren’t healthy and that you might have gum disease:
- Gum recession resulting in teeth appearing longer than normal
- Pain when chewing
- Halitosis (bad breath)
- Gums that bleed often including after brushing your teeth or flossing
- Loose teeth or teeth that fall out entirely
- Swollen gums
- Bright red or purplish gums
- Presence of pus between teeth and gums
- Development of new spaces between teeth
- Change in teeth alignment during biting
- Sensitive gums
What causes gum disease?
- Poor oral hygiene: Poor oral hygiene is the primary cause of gum disease. When you don’t brush your teeth or floss regularly, plaque and tartar can build up, leading to gum inflammation and disease.
- Smoking and tobacco use: Smoking and using tobacco can harm gum tissue, causing inflammation and reducing blood flow to the gums. This can make it harder for the gums to heal from gum disease and can make the disease progress more rapidly.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can make the gums more sensitive and increase the risk of gum disease.
- Medications: Some medications can cause dry mouth, which can lead to gum disease. Medications that cause gum changes, such as overgrowth of gum tissue, can also increase the risk of gum disease.
- Genetics: Some people may be more genetically predisposed to developing gum disease, even with good oral hygiene habits.
- Poor nutrition: A diet lacking in essential nutrients, such as vitamin C, can weaken the immune system and make it more difficult for the body to fight off infections, including gum disease.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and cancer, can increase the risk of gum disease.
It’s important to note that gum disease can also be caused by a combination of these factors. If you are experiencing symptoms of gum disease, such as red, swollen, or bleeding gums, it’s important to see a dentist for an evaluation and treatment.
Gum disease treatment and diagnosis
To determine whether you have gum disease and how severe it is, your dentist will start by reviewing your medical history to identify any factors that could be contributing to your symptoms, such as smoking or taking certain medications that cause dry mouth. They will also examine your mouth to look for plaque and tartar buildup and check for easy bleeding.
Diagnosis
An important step is to measure the pocket depth of the groove between your gums and teeth by placing a dental probe beside your tooth beneath your gumline, usually at several sites throughout your mouth. In a healthy mouth, the pocket depth is usually between 1 and 3 millimetres (mm). Pockets deeper than 4 mm may indicate periodontitis and pockets deeper than 5 mm cannot be cleaned well. In addition, your dentist may take dental X-rays to check for bone loss in areas where your dentist observes deeper pocket depths.
Once your dentist has assessed your condition, they may assign a stage and a grade based on the severity of the disease, the complexity of treatment, your risk factors, and your health.
Clean and Scale
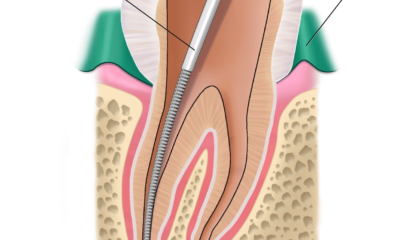
If treatment is necessary, the first line of defence is a clean and scale which can be performed by a dentist or dental hygienist. This is only applicable if the disease is not advanced. The goal is to thoroughly clean the pockets around your teeth and prevent damage to the surrounding bone. Scaling removes tartar and bacteria from your tooth surfaces and beneath your gums, while root planing smooths the root surfaces and removes bacterial byproducts that contribute to inflammation and delay healing or reattachment of the gum to the tooth surfaces.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics can help control a bacterial infection, either topically or orally. However, if the periodontitis is advanced, you may need dental surgery such as flap surgery, soft tissue grafts, bone grafting, or guided tissue regeneration.
Flap Surgery
Flap surgery involves making tiny incisions in your gum so that a section of gum tissue can be lifted back, exposing the roots for more effective scaling and root planing. Soft tissue grafts can help reduce further gum recession, cover exposed roots, and give your teeth a more pleasing appearance.
Bone Grafting
Bone grafting helps prevent tooth loss by holding your tooth in place and serves as a platform for the regrowth of natural bone. Guided tissue regeneration allows the regrowth of bone that was destroyed by bacteria by placing a special piece of biocompatible fabric between existing bone and your tooth.
Remember, the best chance for successful treatment is adopting a daily routine of good oral care, managing health conditions that may impact dental health, and stopping tobacco use.